Planen Sie ein kleineres Projekt und fragen sich, welche der vielen Aspekte und Instrumente auch bei kleinen Projekten berücksichtigt werden sollen? Wir empfehlen mit der Projektskizze im Projektmanagement-Tool zu beginnen. Alternativ dazu können Sie aber auch die Vorlagen unter „Grundlagen“ nutzen:
Zu einem späteren Zeitpunkt können Sie die Projektskizze zu einem Konzept erweitern. Während der Durchführung des Projekts eignen sich insbesondere der interaktive Zeitplan und die Aufgabenliste auch sehr gut für kleinere Projekte. Beim Abschluss des Projekts kann der Schlussbericht entweder direkt im Projektmanagement-Tool oder aber mittels der Word-Vorlage geschrieben werden.
Hier erhalten Sie Hinweise darauf, welche Aspekte einer Projektskizze in einem Konzept ausführlicher thematisiert werden sollten. Die Liste der Elemente ist auch zur eigenen Verwendung als Word-Vorlage verfügbar.
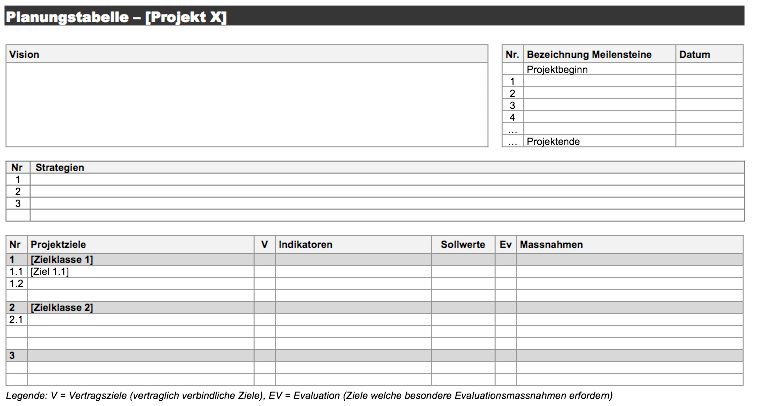
Konzept (Projekt) (pdf) | Konzept Vorlage (Projekt) (docx.zip) | Konzept (Programm) (pdf) | Konzept Vorlage (Programm) (docx.zip)Die Planungstabelle ist das zentrale Instrument für die Planung eines Projekts. Sie dient dazu:
Für eine systematische Reflexion der Qualität von Projekten und Programmen braucht es Kriterien. Die vorliegenden Kriterien beziehen sich auf Interventionsprojekte in der Gesundheitsförderung und Prävention, können aber auch in anderen Projekten zur Anwendung kommen.
Anleitung Qualitätskriterien (pdf)Wenn die Umsetzung eines Projekts/Programms zu Ende ist, ist es an der Zeit, über den Erfolg Rechenschaft abzulegen, die Umsetzung zu reflektieren und die gewonnenen Erkenntnisse und die gemachten Erfahrungen zu dokumentieren.
In der Anleitung erhalten Sie Hinweise darauf, welche Aspekte in einem Schlussbericht ausführlicher thematisiert werden sollte. Die Liste der Elemente ist auch als Word-Vorlage verfügbar.
Schlussbericht (Projekt) (pdf) | Schlussbericht Vorlage (Projekt) (docx.zip) | Schlussbericht (Programm) (pdf) | Schlussbericht Vorlage (Programm) (docx.zip)Hier erhalten Sie Hinweise darauf, welche Elemente in einer Skizze enthalten sein sollten. Die Liste der Elemente ist auch zur eigenen Verwendung als Word-Vorlage verfügbar.
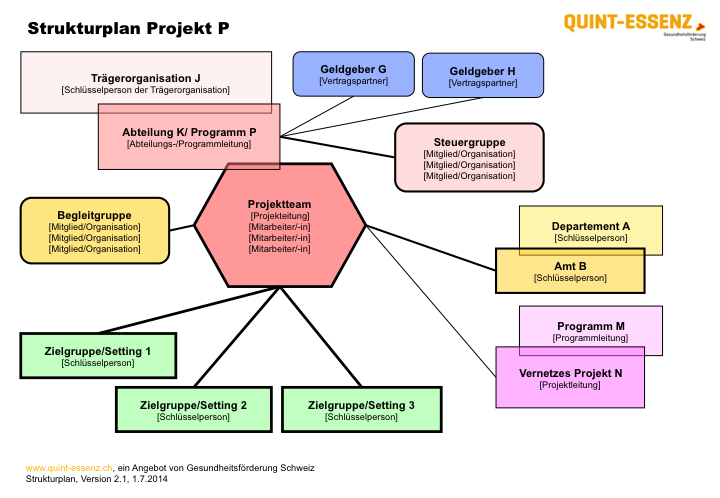
Skizze (Projekt) (pdf) | Skizze Vorlage (Projekt) (docx.zip) | Skizze (Programm) (pdf) | Skizze Vorlage (Programm) (docx.zip)Der Strukturplan wird erstmals in der Skizzierungs- oder Grobplanungsphase entworfen und in späteren Phasen immer wieder zur Hand genommen und überarbeitet. Er dient dazu: