Die Durchführung von Projekten und Programmen der Gesundheitsförderung und Prävention ist sehr anspruchsvoll. Es gilt:
Es ist einerseits viel Detailarbeit auf allen Ebenen gefragt und andererseits gilt es, den Überblick zu wahren.
Das Projekt wird regelmässig systematisch reflektiert und bei Bedarf angepasst.
| Indikatoren | Projektphasen | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| KO | IM | VA | |
Das Projekt ist mittels Meilensteinen in mehrere Etappen gegliedert, für die jeweils eine Feinplanung mit Zwischenzielen gemacht wird. |
|||
Die Entwicklungen des Projekts (in Bezug auf Massnahmen, Zusammenarbeit, Zielerreichung, personelle und finanzielle Ressourcen usw.) und seines Umfelds werden an Meilensteinsitzungen zum Beispiel anhand von Leitfragen oder Kriterien reflektiert. |
|||
Auf der Basis der Reflexionen werden Folgerungen für die nächste Projektetappe abgeleitet und gegebenenfalls Anpassungen vorgenommen. |
|||
Wichtige Aspekte des Projekts sind in nachvollziehbarer Weise dokumentiert.
| Indikatoren | Projektphasen | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| KO | IM | VA | |
Es gibt verbindliche Regeln, was, von wem, auf welche Weise dokumentiert werden soll und wie die Dokumente verwaltet werden. Dabei wird der Datenschutz eingehalten. |
|||
Das Projekt ist umfassend beschrieben (Skizze, Konzept, Zeitplan, Schlussbericht usw.) und die aktuelle Version dieser Dokumente ist den Projektbeteiligten zugänglich. |
|||
Wichtige Beschlüsse sind schriftlich festgehalten. |
|||
Die Erkenntnisse und Erfahrungen (positive und negative) sind so dokumentiert, dass sie den Transfer von Erfahrungen und Wissen in andere Projekte ermöglichen (z. B. Evaluationsberichte, Leitfäden usw.). |
|||
Die interne und externe Kommunikation ist zielgerichtet.
| Indikatoren | Projektphasen | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| KO | IM | VA | |
Es ist verbindlich geregelt, wie der Austausch unter den Projektbeteiligten erfolgen soll und wer, wann, wen, wie, worüber informiert. |
|||
Der Austausch und die Information sind effizient und für alle Projektbeteiligten zufriedenstellend (relevante Informationen, richtiger Zeitpunkt etc.). |
|||
Die Inhalte der externen Kommunikation (Botschaften, Erkenntnisse) werden adressatengerecht aufbereitet und über geeignete Kanäle verbreitet. |
|||
Qualitätskriterien (Projekte) (pdf)
Qualitätskriterien (Projekte) (xlsm.zip)
Das Programm wird auf verschiedenen Ebenen regelmässig systematisch reflektiert und bei Bedarf angepasst.
| Indikatoren | Projektphasen | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| KO | IM | VA | |
Das Programm ist mittels Meilensteinen in mehrere Etappen gegliedert, für die jeweils eine Feinplanung mit Zwischenzielen gemacht wird. |
|||
Die Entwicklungen des Programms (in Bezug auf Massnahmen, Zusammenarbeit, Zielerreichung, personelle und finanzielle Ressourcen usw.) und seines Umfelds werden an Meilensteinsitzungen zum Beispiel anhand von Leitfragen oder Kriterien reflektiert. |
|||
Auf der Basis der Reflexionen werden Folgerungen für die nächste Programmetappe abgeleitet und gegebenenfalls Anpassungen vorgenommen. |
|||
Die Meilensteine des Programms und der Projekte sind aufeinander abgestimmt. |
|||
In jeder Programmetappe werden die Entwicklungen in den einzelnen Projekten und Massnahmen mit den Verantwortlichen systematisch reflektiert. |
|||
Wichtige Aspekte des Programms sind einheitlich und in nachvollziehbarer Weise dokumentiert.
| Indikatoren | Projektphasen | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| KO | IM | VA | |
Es gibt verbindliche Regeln, was, von wem, auf welche Weise dokumentiert werden soll und wie die Dokumente verwaltet werden. Dabei wird der Datenschutz eingehalten. |
|||
Das Programm ist umfassend beschrieben (Skizze, Konzept, Zeitplan, Schlussbericht usw.) und die aktuelle Version dieser Dokumente ist den Programmbeteiligten zugänglich. |
|||
Wichtige Beschlüsse sind schriftlich festgehalten. |
|||
Die Erkenntnisse und Erfahrungen (positive und negative) sind so dokumentiert, dass sie den Transfer von Erfahrungen und Wissen in andere Programme ermöglichen (z. B. Evaluationsberichte, Leitfäden usw.). |
|||
Für die Planung, Steuerung und Evaluation von Projekten werden einheitliche Vorlagen und Instrumente verwendet. |
|||
Die Projekte des Programms und die projektübergreifenden Massnahmen sind so dokumentiert, dass sich die Programmleitung jederzeit über die aktuellen Entwicklungen (Beschlüsse, Änderungen in der Planung usw.) informieren kann. |
|||
Die interne und externe Kommunikation ist zielgerichtet.
| Indikatoren | Projektphasen | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| KO | IM | VA | |
Es ist verbindlich geregelt, wie der Austausch unter den Programmbeteiligten erfolgen soll und wer, wann, wen, wie, worüber informiert. |
|||
Der Austausch und die Information sind effizient und für alle Programmbeteiligten zufriedenstellend (relevante Informationen, richtiger Zeitpunkt etc.). |
|||
Die Inhalte der externen Kommunikation (Botschaften, Erkenntnisse) werden adressatengerecht aufbereitet und über geeignete Kanäle verbreitet. |
|||
Die Kommunikation auf der Programmebene und die Kommunikation auf der Projektebene sind inhaltlich und zeitlich aufeinander abgestimmt. |
|||
Das Programm unterstützt die einzelnen Projekte und fördert übergeordnete Lernprozesse.
| Indikatoren | Projektphasen | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| KO | IM | VA | |
Die Projekte werden bei der Planung, Umsetzung, Evaluation und Valorisierung durch das Programm optimal unterstützt. |
|||
Das Programm stellt regelmässig aktuelles Wissen zur Verfügung, welches von den einzelnen Projekten und Partnern für ihre Aktivitäten genutzt werden kann (wissenschaftliches Wissen, Experten- und Erfahrungswissen). |
|||
Das Programm organisiert den Wissens- und Erfahrungsaustausch unter den Programmbeteiligten und fördert so projektübergreifende Lernprozesse |
|||
Das Programm identifiziert, bewertet und fördert gezielt innovative Ansätze oder Projekte und nutzt sie zur Weiterentwicklung des Programms.
| Indikatoren | Projektphasen | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| KO | IM | VA | |
Es ist definiert, was im Programm unter Innovation verstanden wird und es ist klar geregelt, wer für die Identifikation und Dokumentation von innovativen Potenzialen ausserhalb und innerhalb des Programms zuständig ist. |
|||
Im Rahmen des Programms werden innovative Ansätze getestet, ausgewertet, verbreitet und für die Weiterentwicklung genutzt. |
|||
Für die Bewertung der Qualität von innovativen Projekten werden einheitliche Qualitätskriterien verwendet. |
|||
Qualitätskriterien (Programme) (pdf)
Beurteilungskriterien KAP (pdf)
Qualitätskriterien (Programme) (xlsm.zip)
Beurteilungskriterien KAP (xlsm.zip)
Diese Checkliste dient der Überprüfung der Stärken und Schwächen der Dokumentation in einem Projekt und der Formulierung von entsprechenden Qualitätszielen.
Am besten diskutieren Sie die einzelnen Punkte in Ihrem Projektteam. So lässt sich konkretisieren, was sich bisher bewährt und was sich weniger bewährt hat. Die Liste gibt auch Anregungen, was zusätzlich berücksichtigt werden sollte.
Im Projektkonzept werden in der Regel die geplanten Evaluationsmassnahmen bereits grob skizziert. Das Evaluationskonzept dient nun dazu, diese Aspekte zu vertiefen. Dies ist besonders dann empfehlenswert, wenn die Evaluation von grösserem Umfang ist und das Projektkonzept in Bezug auf die Evaluation noch viele Fragen offen lässt. Wenn ein externes Institut mit der Evaluation betraut werden soll, dann empfiehlt es sich in jedem Fall, als Basis für die Diskussion mit entsprechenden Instituten und für Offertenanfragen ein Evaluationskonzept zu entwerfen. Dadurch ist man angehalten, sich intensiver mit den Fragen der Evaluation auseinanderzusetzen und die eigenen Erwartungen und Fragestellungen zu explizieren. Auch in Bezug auf die Methodik ist es hilfreich, sich bereits erste Gedanken zu machen, selbst wenn die Kenntnisse diesbezüglich begrenzt sein sollten. Das Evaluationsinstitut wird dabei helfen, die richtige Methodik zur Beantwortung der Evaluationsfragen zu finden.
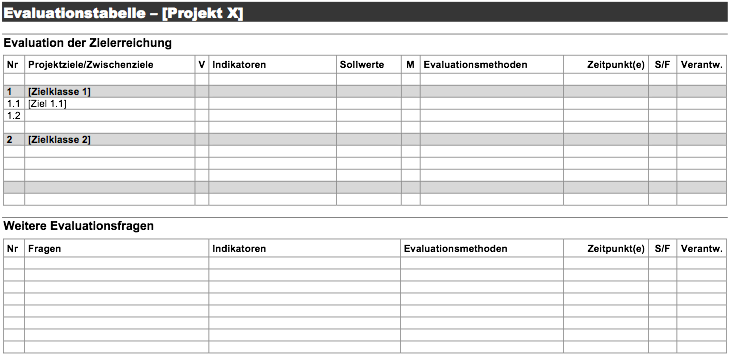
Anleitung (pdf) | Vorlage (doc.zip)In der Evaluationstabelle wird festgehalten, wie die Erreichung derjenigen Projektziele und Zwischenziele überprüft werden soll, die evaluiert werden müssen. Die systematische Überprüfung der Wirkungen des Projekts dient der Projektsteuerung sowie dem Nachweis des Projekterfolgs. Neben den Zielen werden in der Evaluationstabelle auch allfällige weitere Evaluationsfragen aufgeführt. Auf dieser Basis werden Evaluationsform, Erhebungsmethoden, Fristen und Verantwortlichkeiten festgelegt.
Die Kollegiale Beratung ist ein Instrument für die Intervision (Austausch und Beratung unter Fachleuten). Sie dient dazu, einer Kollegin oder einem Kollegen bei der Lösung eines Problems zu helfen. Ausgehend von einer strukturierten Fall- oder Problemschilderung der Person A versuchen die beratenden Kolleginnen und Kollegen in einem strukturierten Vorgehen mit ihrer Erfahrung und ihrem Wissen zur Problemlösung beizutragen.
Anleitung (pdf)Meilensteinsitzungen sind ein wichtiges Element der Projektsteuerung. An ihnen wird eine strukturierte Rückschau der bisherigen Projektarbeit vorgenommen, werden Zwischen- und Qualitätsziele reflektiert, die Stimmung im Team beurteilt und die weiteren Schritte geplant. Die Fragen unterstützen die Vorbereitung und Leitung der Meilensteinsitzungen.
Leitfragen (pdf)Projekte der Gesundheitsförderung und Prävention agieren nicht isoliert. Vielfältige rechtliche, politische, soziale, ökonomische und kulturelle Umweltfaktoren, aber auch andere Akteure im Feld beeinflussen deren Entwicklung und tragen dazu bei, dass die Umsetzung häufig nicht so verläuft wie geplant. Zudem bestimmen die Zielgruppen den Projektverlauf entscheidend mit, insbesondere bei einem hohen Partizipationsgrad. Wenn neue Interventionsansätze getestet oder Projekte auf neue Kontexte übertragen werden, ist der Grad an Ungewissheit besonders hoch. Projekte sind also vielfältigen äusseren Faktoren ausgesetzt, welche den Verlauf und den Erfolg eines Projekts nicht nur begünstigen, sondern auch gefährden können. Aber auch innerhalb eines Projektes sind schwer vorhersehbare Entwicklungen, wie beispielsweise Wechsel im Projektteam, nicht selten.
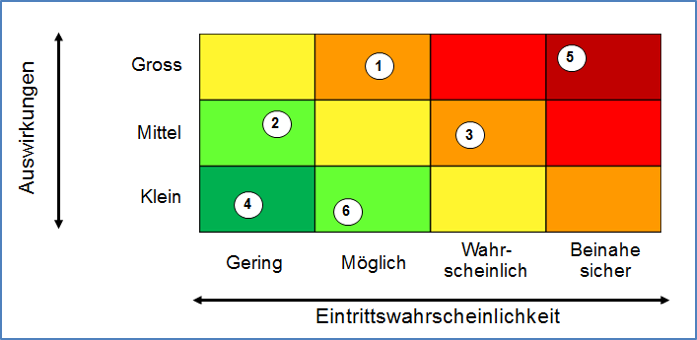
Die Risikoanalyse dient dazu, derartige Risiken zu identifizieren, zu beschreiben und zu bewerten. Auf dieser Grundlage können Massnahmen zur Reduktion oder gar Verhinderung der Risiken festgelegt werden. Die Risikoanalyse ist exemplarisch für Projekte ausformuliert, kann analog aber auch für Programme und Organisationen durchgeführt werden. Idealerweise wird die Risikoanalyse zunächst von den Teammitgliedern (und evtl. weiteren Anspruchsgruppen) einzeln ausgefüllt und danach in einer Besprechung verglichen und zu einer Synthese zusammengefasst.
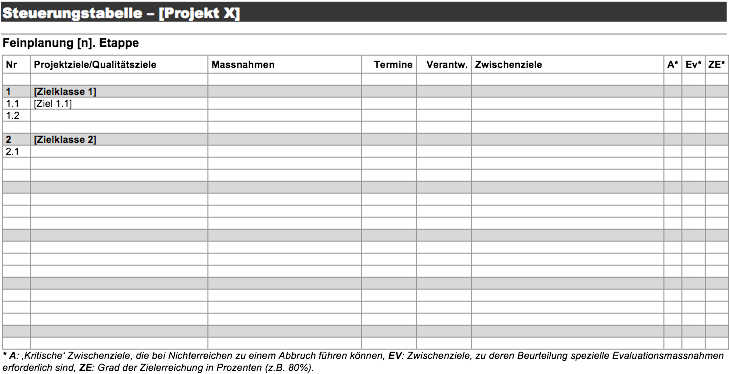
Anleitung (pdf) | Vorlage (docx.zip)Die Steuerungstabelle nimmt in der Implementierungsphase eines Projekts eine zentrale Rolle ein. Sie dient dazu:
Das Stimmungsbarometer dient zum Identifizieren von Faktoren, die für ein Motivationstief verantwortlich sein können. Oder es kann Diskrepanzen zwischen Erwartungen und Hoffnungen oder Veränderungen in der Haltung bestimmten Themen gegenüber aufzeigen. Es bietet Ansatzpunkte zum Angehen und Überwinden von Schwierigkeiten.