Bei Gesundheitsförderung und Prävention handelt es sich um Interventionen in komplexe sozial-räumliche Systeme. Aufgrund der hohen Dynamik im Feld und der Unterschiedlichkeit der Kontexte, in welche interveniert wird, sind standardisierbare Vorgehensweisen eher die Ausnahme und die Komplexität erschwert klare, verallgemeinerbare Aussagen darüber, was der „optimale“ bzw. „beste“ Ansatz ist.
Werte, Wissen und Kontext
Gesundheitsförderung Schweiz hat in Zusammenarbeit mit nationalen und internationalen Partnern einen Rahmen für Best Practice in der Gesundheitsförderung und Prävention definiert, der als Referenz für Interventionsplanung und Entscheidfindung in der Gesundheitsförderung und Prävention dient. Mit seinen drei Dimensionen (Werte, Wissen, Kontext) soll er ethisch verantwortliches, im breiteren Sinne wissensbasiertes und zugleich kontextsensibles Entscheiden und Handeln fördern.
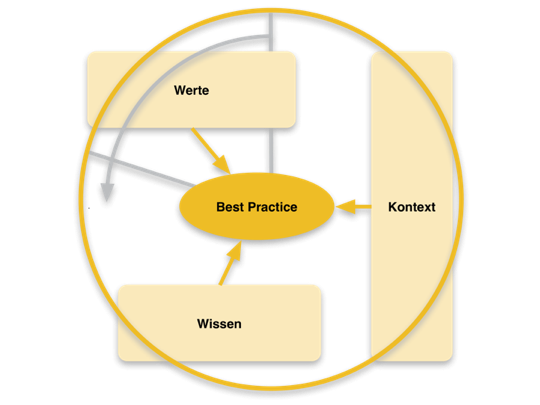
Die Umsetzung des Best Practice-Ansatzes hilft, die Wirksamkeit von Interventionen zu erhöhen, wenn:
- die Grundwerte und Prinzipien von Public Health und Gesundheitsförderung systematisch reflektiert und bei Interventionen angemessen berücksichtigt werden
- wissenschaftliches Wissen für die Praxis recherchiert, aufgearbeitet und genutzt wird, wichtiges Praxis- und Expert/-innenwissen berücksichtigt und durch gezielte Evaluation zur Stärkung des wissenschaftlichen Wissens (Evidenz in der Gesundheitsförderung und Prävention beiträgt
- die jeweiligen Kontextbedingungen reflektiert, die Übertragung von Interventionen in andere Kontexte sorgfältig geprüft und Interventionen entsprechend adaptiert werden.
Entsprechend heißt Best Practice in Gesundheitsförderung und Prävention, „die Werte und Prinzipien von Gesundheitsförderung und Public Health systematisch zu berücksichtigen, auf das aktuelle wissenschaftliche Wissen und Experten-/Erfahrungswissen aufzubauen, die relevanten Kontextfaktoren zu beachten, sowie die beabsichtigten positiven Wirkungen erreicht und negative Wirkungen vermieden zu haben“ (Gesundheitsförderung Schweiz, 2010, S. 7).
Eine allgemeingültige, kontextunabhängige Liste von „Best Practice“-Interventionen im Sinne von eindeutigen ‚Rezepten’ für die Praxis ist in den meisten Handlungsfeldern der Gesundheitsförderung und Prävention nicht möglich. Interventionen müssen im neuen Umfeld jeweils mit den Anspruchsgruppen reflektiert und an die veränderten Kontextbedingungen angepasst werden.
Umsetzung
Die Umsetzung des Best-Practice-Rahmens verlangt von Fachpersonen eine systematische, wiederkehrende Reflexion oder kritische Hinterfragung einer Entscheidfindung und der Planung, Umsetzung und Evaluation von gesundheitsfördernden oder präventiven Aktivitäten (vgl. Abbildung). Dies erfolgt entlang der drei Best-Practice-Dimensionen und der dazugehörigen Kriterien und Indikatoren, ähnlich einem Radarstrahl, der zur Flugsicherung wiederholt über den Himmel streicht. Diese Forderung nach periodisch wiederkehrender systematischer Reflexion entspricht den Entwicklungszyklen, die laut quint-essenz typisch für einen Projektverlauf sind.
Die Qualitätskriterien von quint-essenz berücksichtigen und operationalisieren im Wesentlichen auch die zentralen Aspekte der Best Practice-Kriterien. Die systematische Berücksichtigung der Qualitätskriterien von quint-essenz bei der Planung, Durchführung, Evaluation und Reflexion von Interventionsprojekten deckt damit auch die wesentlichen Aspekte der Best Practice-Kriterien ab.
Literaturhinweise
-
Gesundheitsförderung Schweiz (Hrsg.) (2010). Best Practice. Ein normativer Handlungsrahmen für optimale Gesundheitsförderung und Krankheitsprävention. Bern: Gesundheitsförderung Schweiz.
Link/Download
-
Broesskamp-Stone, Ursel (2009). Gute, viel versprechende, beste Praxis? Der Best-Practice-Rahmen für Gesundheitsförderung und Prävention. In: Kolip, Petra; Müller, Veronika (Hg.) Qualität von Gesundheitsförderung und Prävention. Handbuch Gesundheitswissenschaften, S. 115-136. Bern: Huber.
-
Broesskamp-Stone, Ursel (2008). Best-Practice in der Gesundheitsförderung und Prävention – Konzept und Leitlinien für Entscheidfindung und fachliches Handeln. In: Spicker I. & Sprengeis G. Gesundheitsförderung stärken. Kritische Aspekte und Lösungsansätze, S.79-94. Wien: Facultas.
- Systematische Reflexionen sind zeitaufwändig und der Projektalltag lässt dies kaum zu
- Es ist sehr schwierig, mit den beteiligten Akteuren Wertefragen zu diskutieren, diese sind in der Regel nicht vorrangig
- Es ist einfacher, ein einmal bewährtes Projekt ein zu eins auf verschiedene Kontexte zu übertragen als jedes Mal neu anzupassen
- Durch die fundierte Reflexion der Werte und Prinzipien von Public Health und Gesundheitsförderung bleiben grundlegende Anliegen wie Chancengleichheit und Autonomieförderung nicht blosse Schlagworte sondern fliessen in die Planung, Entscheidfindung und Evaluation von Interventionen ein
- Ein kontextsensibles Vorgehen trägt den Besonderheiten der einzelnen Settings und Zielgruppen Rechnung und verhindert das unreflektierte Überstülpen unangemessener Programme.
- Mit der Berücksichtigung aktuellen wissenschaftlichen Wissens und weiterem Praxis- und Expertenwissen stellen Sie Ihr Gesundheitsförderungs- und Präventionsvorhaben auf eine solide professionelle Basis.
- Schenken Sie den drei Dimensionen Werte, Wissen und Kontext ausreichend Beachtung, egal ob Sie sich mit Strategieentwicklung, Projektplanung oder mit Evaluationsfragen befassen.
- Kennen die wichtigsten Akteure die Werte und Prinzipen der Gesundheitsförderung und wurde eine Auseinandersetzung darüber geführt, inwieweit diese mit dem geplanten oder aktuell realisierten Vorhaben?
- Werden die Ergebnisse und Erfahrungen aus Ihrem Projekt so aufgearbeitet und verbreitet, dass auch andere davon profitieren können?