Heute ist allgemein anerkannt, dass die Gesundheit der Menschen stark durch ihre Lebensbedingungen sowie durch die Lebens- und Verhaltensweisen beeinflusst wird. Diese Einflüsse werden, im Gegensatz zu den biologisch-genetischen Faktoren, mit dem Begriff „Determinanten der Gesundheit“ benannt. Determinanten der Gesundheit können nicht isoliert voneinander betrachtet werden. Sie wirken in vielfältigen, sich gegenseitig beeinflussenden Prozessen. Eine individuelle Verhaltensweise wie beispielsweise Rauchen ist beeinflusst vom Lebensstil- der wiederum geprägt ist von den Lebensbedingungen einer Person.
Das Interesse an den Determinanten der Gesundheit hat in den letzen Jahren zugenommen. Das zeigt sich daran, dass Länder angefangen haben, ihre Gesundheitsberichterstattung auf Determinanten der Gesundheit statt an Gesundheitsrisiken zu orientieren. Für weltweites Interesse hat auch die 2005 von der WHO gegründete Kommission (CSDH) für Soziale Determinanten der Gesundheit unter der Leitung von Michael Marmot gesorgt. Auftrag dieser Gruppe war, Evidenzen zu finden, wie gesundheitliche Ungleichheit verringert werden kann und was zu tun ist, damit weltweit diesbezüglich Fortschritte erreicht werden können. Der Schlussbericht wurde 2008 von der Gruppe unter dem Titel „Closing the gap in a generation. Health equity through action on the social determinants of health“ publiziert.
Begründet wird das zunehmende Interesse an den Sozialen Determinanten der Gesundheit damit, dass sie als adäquate Antwort auf die sich zu Beginn des 21. Jahrhunderts verändernden Lebens- und Arbeitsbedingungen gesehen werden, die durch Globalisierung und Individualisierung zu einer Zunahme von chronischen und psychischen Krankheiten geführt haben.
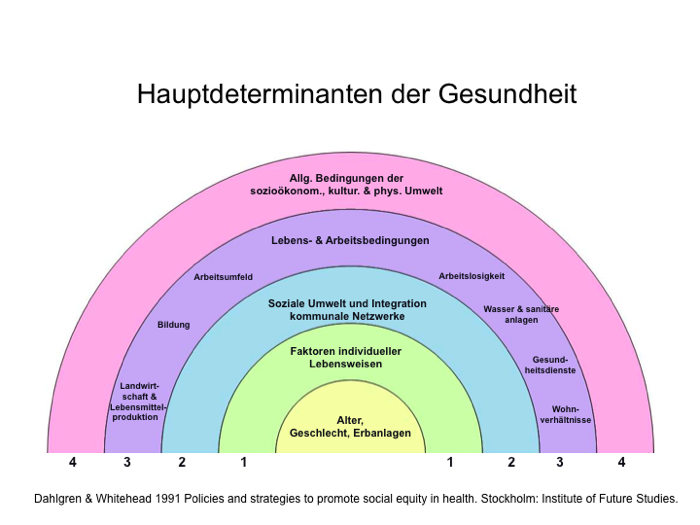
Als wichtige Determinanten werden unter anderem Einkommen und sozialer Status, soziale Unterstützung , soziale Netzwerke, Bildung, soziale Lebensumwelt, Gender und kulturelles Umfeld gesehen.
Weitgehend fehlen noch Erklärungen, wie sich die verschiedenen Faktoren gegenseitig beeinflussen und welche Wirkungspfade unter welchen kontextuellen Bedingungen entscheidend sind.
Für die Praxis bedeutet die Fokussierung auf Determinanten der Gesundheit ein verstärktes Umdenken. Die bisherige Betonung auf individuelle Verhaltensweisen muss stärker in Richtung Verhältnisprävention unter Berücksichtigung der gesundheitlichen Ungleichheit gelenkt werden. Der Einbezug des soziokulturellen Kontextes bei Interventionen erhält eine zentralere Bedeutung. Dafür braucht es Grundlagen, eine Gesundheitsberichterstattung, die konsequent auf den Gesundheitsdeterminanten aufgebaut ist. Diese liefert nicht nur die notwendigen Grundlagen für die Umsetzung, sondern ermöglicht durch Evaluationen auch Rückschlüsse, ob Interventionen Veränderungen bewirkt haben. Die Forschung ist insbesondere für die Erklärungen der komplexen Zusammenhänge zwischen Lebenslage und Verhaltensweisen herausgefordert. Schlussendlich ist die Politik für die Entwicklung von gesellschaftlichen Rahmenbedingungen gefragt. Nicht nur das Gesundheitswesen, sondern alle Sektoren sind an der positiven Beeinflussung der Sozialen Determinanten der Gesundheit beteiligt. Dazu sind Verfahren für eine multisektorale Zusammenarbeit zu entwickeln und die konsequente Umsetzung einer Health in All Policy wichtig.